What is NMN? Do You Want to Stay Young and Fight Aging?
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a nucleotide derived from ribose, nicotinamide, nicotinamide riboside and niacin.
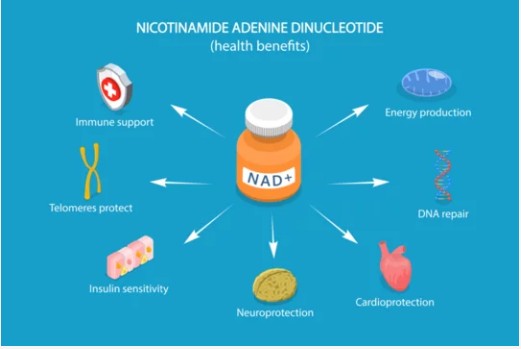
In humans, several enzymes use NMN to generate nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH).
Since NADH serves as a crucial cofactor for mitochondrial processes, longevity proteins like sirtuins, and DNA repair enzymes like PARP, NMN has emerged as a potential neuroprotective and anti-aging agent. This has been validated through studies in animal models.
By increasing NAD+ levels, NMN helps reverse aging at the cellular level by preventing mitochondrial decline, making it a popular choice in anti-aging products. However, because the NAD+ molecule is too large to pass through cell membranes, it cannot be directly consumed to increase NAD+ levels in the body.
The NAD+/NADH ratio is a critical marker of cellular health. When this ratio becomes imbalanced—particularly when it decreases—several cellular issues can arise, like impaired cellular energy production and dysfunction in mitochondrial activity etc.
Monitoring and restoring the NAD+/NADH ratio can help manage diseases and conditions caused by its imbalance. Fortunately, some testing services are available to measure your NAD+/NADH ratio, and you can supplement with the right nutrients with this test to balance your body healthily.
Aging Factors and Improvement Methods
- Aging Factors
- Genetic Factors
Certain gene variations may affect cellular repair and antioxidant capacity, increasing the risk of aging. - Environmental Stress
Factors such as UV radiation, pollutants, smoking, and unhealthy dietary habits increase free radical production, accelerating cellular aging. - Metabolic Abnormalities
Issues such as insulin resistance, obesity, and chronic inflammation disrupt normal cellular function. - Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Decline
Reduced mitochondrial function impairs energy production, leading to systemic aging. - DNA Methylation Abnormalities
With aging, DNA methylation patterns become abnormal, potentially causing gene dysregulation and promoting age-related diseases.
2. Improvement Methods
- Dietary Regulation
Consume antioxidant-rich foods, such as berries, edamame, and dark-colored vegetables, while avoiding high-sugar and high-fat diets. - Exercise Routine
Regular exercise enhances metabolism, reduces chronic inflammation, and strengthens mitochondrial function. - Supplementation with NMN or NAD+ Precursors
Boosts the NAD+/NADH ratio, activates sirtuins, and improves cellular function. - Stress Management and Adequate Sleep
Reducing stress hormones (e.g., cortisol) and improving sleep quality can help slow physiological aging. - Avoiding Environmental Toxins
Minimize exposure to pollutants and tobacco to protect cells from oxidative stress.
DNA Methylation Clock Testing
- What is the Methylation Clock?
The DNA methylation clock is a tool based on DNA methylation patterns at specific CpG sites to estimate biological age. It reflects the aging level of cells and tissues, providing a more accurate indicator than chronological age and is closely related to health and longevity. - Testing Method (Epson Biomed offers methylation clock testing services—please call for consultation)
- Testing Process
- Sample Collection: A small amount of whole blood is collected, and DNA is extracted.
- Methylation Analysis: Specific CpG sites related to age are selected, and high-throughput technology is used to detect the methylation levels of these sites.
- Data Modeling: The results are processed using artificial intelligence algorithms to convert methylation data into an individual’s biological age.
By supplementing with NMN, the NAD+/NADH ratio can be elevated, thereby improving mitochondrial function, and enhancing cellular performance. This process helps prevent aging and keeps our bodies in a youthful state.
References
- Roger Lee, Roger (2023). Different Expressions of NMN Across Human Organs.
- Loss of epigenetic information as a cause of mammalian aging Yang, Jae-Hyun et al. Cell, Volume 186, Issue 2, 305 - 326.e27