EpiSante Biomedical | Establishment and Consulting of LDTs Lab | DNA methylation analysis | cancer management
Products and Services
- Testing Service
- 2nd Generation of Liver Cancer Early Screening-MPMEpiSante Biomedical - 2nd Generation of Liver Cancer Early Screening-LiverES | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- Prognosis of liver Cancer Resection-LiverRPEpiSante Biomedical - Prognosis of liver Cancer Resection-LiverRP | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- Prognosis and Monitoring of Liver Cancer Ablation-LiverAMEpiSante Biomedical - Prognosis and Monitoring of Liver Cancer Ablation-LiverAM | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- LiverMeth-Liver Cancer Gene Methylation TestEpiSante Biomedical - LiverMeth-Liver Cancer Gene Methylation Test | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- Global DNA Methylation TestEpiSante Biomedical - Global DNA Methylation Test | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- MethClock-Biological Age Anti-aging TestEpiSante Biomedical - Global DNA Methylation Test | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- Establishment and Consulting of LDTs LabEpiSante Biomedical - Establishment and Consulting of LDTs Lab | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- Reagents and KitsEpiSante Biomedical - Reagents and Kits | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- Customized ServiceEpiSante Biomedical - Customized Service | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
CancerMeth-Cancer Gene Methylation Test
DNA methylation regulates many normal physiological functions, such as embryonic development, genomic imprinting, X-chromosome inactivation in females, and maintaining genomic stability. If DNA methylation is abnormal, it can cause many diseases, including metabolic diseases (diabetes), mental disorders (schizophrenia), autoimmune diseases (lupus), asthma, aging, and cancer. Studies have found that abnormal changes in DNA methylation can be detected at the early stages of cancer, even before obvious symptoms appear, making methylation markers a valuable tool for early cancer screening.
Methylation Markers Are More Specific than Protein Markers
Due to the unique methylation patterns of different cancers, DNA methylation markers are highly specific for cancer diagnosis. In contrast, serum protein markers are widely expressed in various types of cancers and have lower specificity. Moreover, protein molecules are less stable, whereas methylation markers provide more stable and reliable information. This makes DNA methylation markers highly valuable and promising in cancer research and clinical applications.
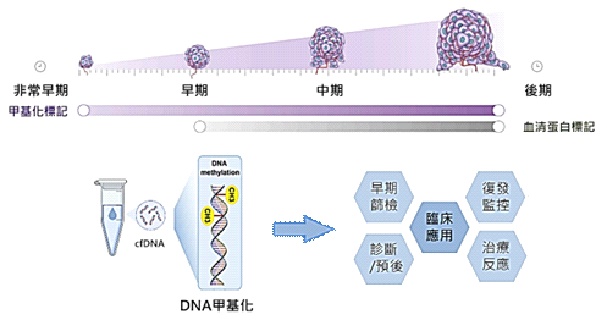
Methylation Testing in Liquid Biopsy Detects Cancer at a Very Early Stage
CancerMeth detection technology detects the methylation of tumor suppressor genes on ctDNA (circulating tumor DNA) released into the blood by tumor cells. In the early stages of cell carcinogenesis, many genes undergo abnormal methylation. Therefore, detecting the methylation of ctDNA released by tumors in the blood helps in the early detection of cancer and monitoring of the disease.
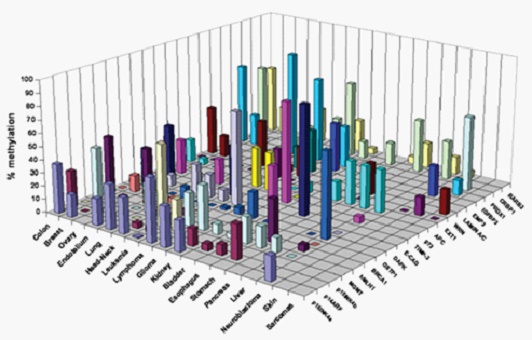
CancerMeth can detect 16 types of cancer, including lung cancer, liver cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, pancreatic cancer, stomach cancer, ovarian cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, thyroid cancer, renal cell carcinoma, glioblastoma, endometrial cancer, cervical cancer, and esophageal cancer.
What's the Difference between Methylation Testing and Genetic Testing
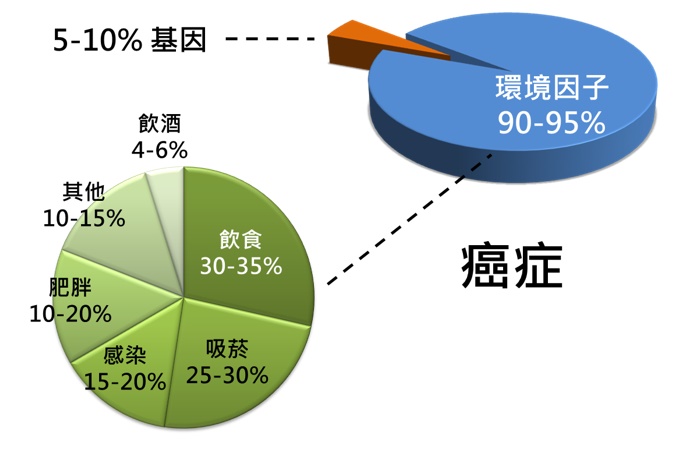
Recent studies suggest that only about 5-10% of cancers are linked to genetic mutations, while 90-95% are attributed to environmental factors such as diet, smoking, alcohol consumption, and obesity. These environmental factors influence gene expression through DNA methylation. Unlike genetic testing, which primarily predicts lifetime cancer risk based on specific gene mutations, methylation is reversible and is therefore better suited for regular monitoring. It is currently the most popular and mainstream biomarker for cancer.
Who needs the testing?
- People over 50 years old
- people with a family history of cancer
- high-risk cancer groups
- people undergoing stem cell therapy
