EpiSante Biomedical | MethClock-Biological Age Anti-aging Test | DNA methylation analysis | cancer management
Products and Services
- Testing Service
- 2nd Generation of Liver Cancer Early Screening-MPMEpiSante Biomedical - 2nd Generation of Liver Cancer Early Screening-LiverES | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- Prognosis of liver Cancer Resection-LiverRPEpiSante Biomedical - Prognosis of liver Cancer Resection-LiverRP | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- Prognosis and Monitoring of Liver Cancer Ablation-LiverAMEpiSante Biomedical - Prognosis and Monitoring of Liver Cancer Ablation-LiverAM | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- CancerMeth-Cancer Gene Methylation TestEpiSante Biomedical - CancerMeth-Cancer Gene Methylation Test | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- LiverMeth-Liver Cancer Gene Methylation TestEpiSante Biomedical - LiverMeth-Liver Cancer Gene Methylation Test | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- Global DNA Methylation TestEpiSante Biomedical - Global DNA Methylation Test | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- Establishment and Consulting of LDTs LabEpiSante Biomedical - Establishment and Consulting of LDTs Lab | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- Reagents and KitsEpiSante Biomedical - Reagents and Kits | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
- Customized ServiceEpiSante Biomedical - Customized Service | DNA methylation | methylation, cancer testing, liver cancer, liver testing, liquid biopsy, liver prognosis, liver ablation, liver resection, immunotherapy, cell therapy
MethClock-Biological Age Anti-aging Test
DNA methylation patterns change during the aging process and disease development. These changes can be used to assess and evaluate the aging and disease status of human organs and systems. Currently, DNA methylation patterns are widely used as a measure of biological age, termed the "methylation clock." Unlike chronological age, which is calculated from birth, biological age provides a better measure of an individual's bodily functions and aging rate. Due to factors such as lifestyle and genetics, biological age may differ from chronological age. A 50-year-old with healthy habits may have a younger biological age than a 40-year-old who smokes and drinks daily.

A randomized controlled trial demonstrated that an 8-week dietary and lifestyle intervention (including a healthy diet, sleep, exercise, relaxation techniques, and supplementation with probiotics and plant-based nutrients) resulted in a 3.23-year reduction in biological age as assessed by the methylation clock compared to a control group without intervention (p = 0.018). (Aging 2021;13:9419–9432)
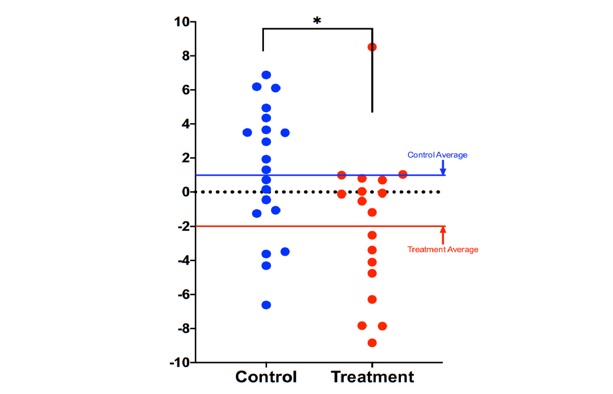
Leukemia patients have a higher physiological age compared to the general population, while individuals who have received NK cell infusion have a lower physiological age.

AML: Acute myeloid leukemia
H and LX: Healthy people
T:people with NK cell infusion
Who needs the testing?
- For those seeking to maintain good health and a youthful appearance
- People under high stress and experiencing job burnout
- Individuals lacking energy and feeling frequently fatigued
- Those undergoing anti-aging treatments
- People with weakened immune systems and frequent illness
- Individuals engaged in long-term hazardous work that indirectly harms the body
